Clustering provides the mechanism to group more than one server, Queue manager as a whole so that client treats as a single entity.
Advantages :-
- Failover
- Load-balancing
- Scalability
- Easy to administrator
How to achieve clustering in Websphere queue manager
There is a concept of repository which cluster software maintain about the meta-data of servers, queue managers, shared queues, etc.
Repository is nothing but type-specification of queue-manager.
Types:-
- Full repository
- Partial repository
Full Repository :- holds cluster configurable information. If queue manager marked at full repository in cluster went down then whole cluster went down. So, at the design time better to assign 2 queue manager as full repository so that another will take charge.
Partial Repository :- QM marked as partial repository acts as client of full repository. If this need any meta-data or configuration , then it ask to full repository QM though command queue.
Note :- more than 1 queue manager marked as queue manager do syncing among each other, so if we make more than 2 QM as full repository then lots of syncing take computer processing resulting performance degradation. So, best is 2 QM assigned as full repository. Other will be partial.
Steps involved in clustering.
- In your enterprise, identify the at most 2 queue manager which will be marked as full repository.
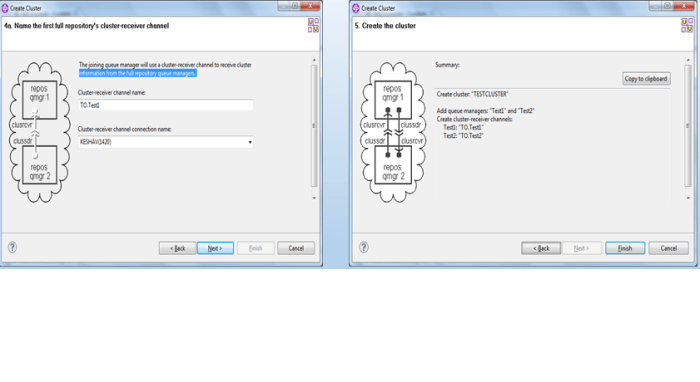
- Define cluster-sender and cluster-receiver channel in full repository.
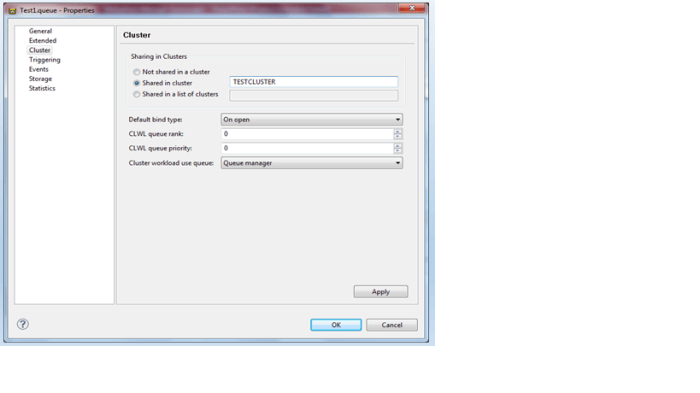
- Define a cluster local queue.
Create a Queue manager Test1 (TCP Port 1420)

Create another queue manager Test2 (TCP port 1421)

Create a cluster sender channel named TO.TEST2 in TEST1 Queue manager
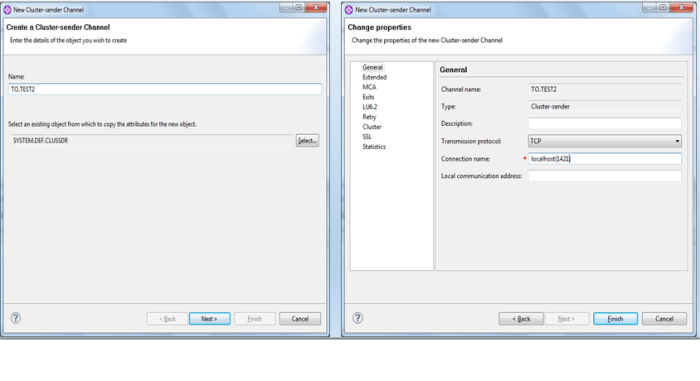
Create a cluster receiver named TO.TEST1 inside TEST1 queue manager
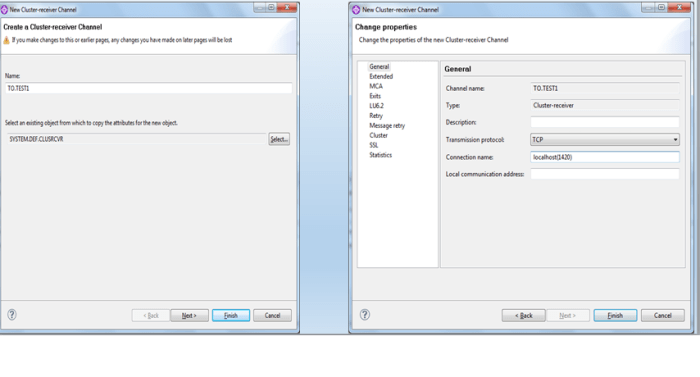
Create a cluster sender channel named TO.TEST1 inside Test2 queue manager

Create a cluster receiver channel named TO.TEST2 inside Test2 queue manager

Create a cluster named TESTCLUSTER
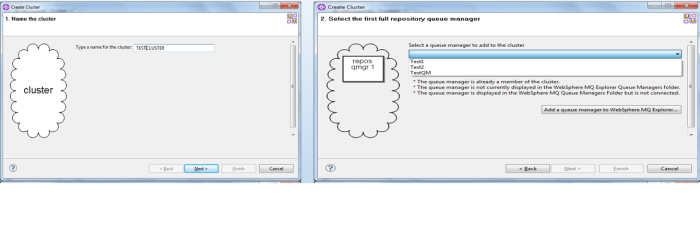
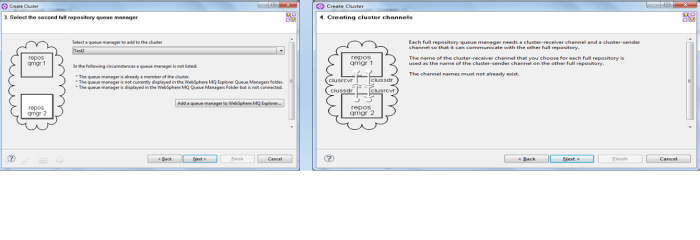
Create another queue manager Test3 and assigned it as partial repository
